I often think about augmented reality as a promise that took longer than expected to mature. For years, AR meant floating labels, novelty filters, or carefully scripted overlays that worked beautifully in demos but struggled in real environments. Ark Augmented Reality, commonly called Ark AR, signals a different direction. It represents a shift from static augmentation toward systems that reason about the world they see and adapt their behavior dynamically.
Ark AR refers to a family of platforms and research driven frameworks that combine real time spatial mapping with machine learning and cloud intelligence. In the first moments of interaction, the system scans a physical environment through cameras and sensors. Within milliseconds, it understands surfaces, objects, lighting, and context. Digital content does not simply appear. It anchors, adjusts, and responds as if it belongs there.
This matters because the next phase of AR adoption depends on reliability and intelligence, not spectacle. Businesses want training systems that adapt to changing layouts. Educators want lessons that respond to student interaction. Artists want narratives that evolve rather than repeat. Ark AR addresses these needs by integrating AI driven knowledge inference into the core of AR pipelines.
At its most ambitious, Ark AR moves beyond prebuilt scenes. It draws on large foundation models, cloud based assets, and low latency rendering to generate or modify AR experiences on the fly. The result is an augmented world that feels less scripted and more alive, capable of handling unfamiliar spaces without retraining or manual setup.
From Overlays to Understanding
Traditional augmented reality systems rely on predefined anchors. A marker, a GPS coordinate, or a manually placed object tells the system where digital content should live. This approach works well in controlled environments but breaks down when conditions change.
Ark AR systems approach the problem differently. They treat the physical world as a dynamic dataset. Using simultaneous localization and mapping techniques refined over the past decade, the device constructs a spatial model in real time. On top of this foundation, machine learning models interpret what those surfaces represent.
According to research published by Azuma in Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, early AR struggled with registration accuracy and drift. Ark AR builds on decades of progress in visual inertial odometry and depth sensing, dramatically improving stability.
Low latency rendering is critical here. Studies from NVIDIA’s graphics research group show that perceived realism in AR drops sharply when latency exceeds 20 milliseconds. Ark AR platforms rely on optimized pipelines and cloud assisted computation to stay within this threshold, even when scenes grow complex.
This evolution from overlay to understanding changes user expectations. The system no longer waits for explicit instructions. It infers intent from context.
Read: Quick Links Explained: Tools, Extensions, Deep Linking
Core Technology Behind Ark AR
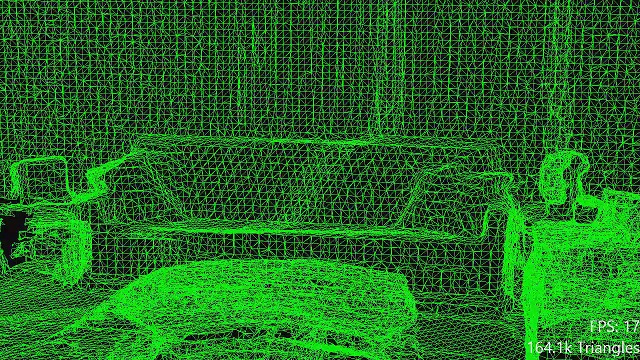


At the technical level, Ark AR combines several mature technologies into a cohesive stack. Spatial mapping provides geometry. Computer vision identifies objects and surfaces. Machine learning models classify and predict. Cloud infrastructure supplies scale.
A typical Ark AR pipeline begins with sensor fusion. Cameras, gyroscopes, and accelerometers feed data into a real time model of the environment. Surface detection algorithms identify planes, edges, and volumes. Object recognition models trained on large datasets classify what the system sees, from furniture to machinery.
Cloud based asset management plays a crucial role. Rather than storing every possible model locally, Ark AR systems stream assets as needed. This approach reduces hardware requirements and enables updates without reinstalling applications.
Developer SDKs sit on top of this infrastructure. These toolkits allow teams to define behaviors rather than fixed scenes. Instead of placing an object at coordinates, developers specify rules. If the system detects a workbench, display safety instructions. If a user gestures toward a component, reveal internal layers.
As Tim Cook noted in a 2016 interview with The Washington Post, “AR can be very interesting, but it has to be grounded in reality.” Ark AR operationalizes that grounding through inference.
Knowledge Driven Augmentation
A defining concept within Ark AR research is knowledge inference. Rather than relying solely on sensor data, the system draws from pretrained foundation models to interpret and generate content.
The ArK framework, short for Augmented Reality with Knowledge Interactive Emergent Ability, formalizes this idea. Introduced in academic literature in the early 2020s, ArK proposes an “infinite agent” that transfers knowledge from large models into AR environments without task specific retraining.
This agent acts as a mediator. It queries language and vision models to understand context, then translates that understanding into AR actions. For example, if a user asks how a machine works, the system can generate an explanatory overlay even in an unseen environment.
Researchers describe this process as cross modality reasoning. Text, images, and sensor data merge into a shared representation. Macro behaviors govern high level goals, while micro actions handle rendering and interaction.
A 2023 arXiv paper demonstrated that ArK generated higher quality scenes than baseline AR systems when evaluated on dynamic tasks. The key advantage was adaptability. The system did not need predefined templates.
Applications in Business and Industry
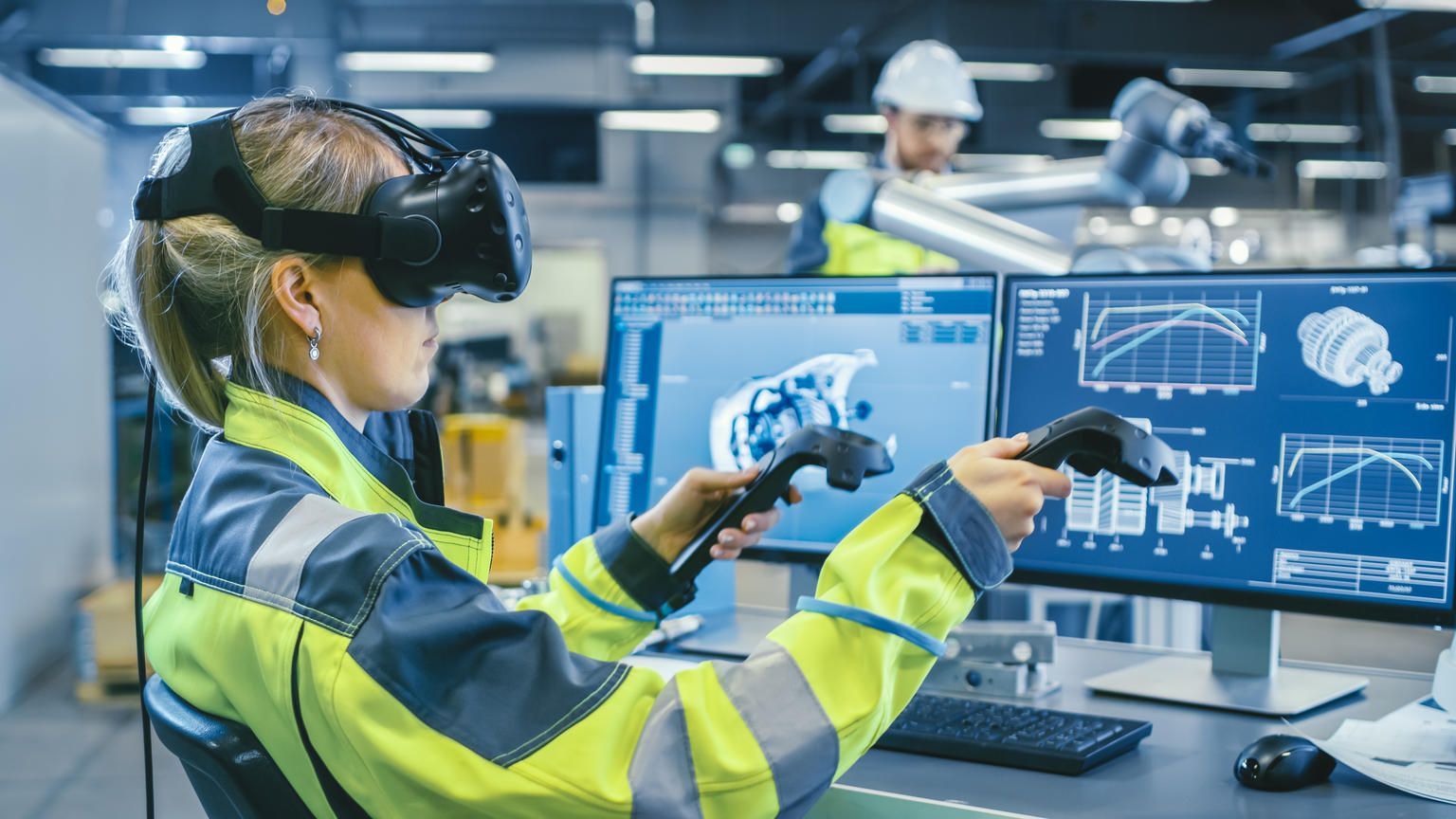



Enterprise adoption is where Ark AR shows immediate value. Training programs benefit from contextual guidance. Instead of generic instructions, workers see overlays tailored to their specific environment.
Manufacturing firms have experimented with AR assisted assembly for years. According to a 2019 Harvard Business Review analysis, AR guided training reduced error rates and improved retention. Ark AR enhances this model by adapting instructions when layouts or equipment change.
Marketing campaigns also leverage Ark AR for interactive engagement. Consumers can visualize products in their own spaces, with content that responds to lighting and scale. Analytics integrated into these experiences provide data on interaction patterns.
In logistics and facilities management, Ark AR overlays real time data onto physical assets. Maintenance schedules, sensor readings, and safety alerts appear where they are most relevant.
The common thread is scalability. Ark AR reduces the need for specialized hardware. Standard smartphones and tablets become portals to intelligent augmentation.
Arts, Performance, and Storytelling
In creative fields, Ark AR opens new narrative possibilities. Mixed reality theater projects such as “An Ark” blend live performers with digital elements viewed through AR glasses. The audience sees a layered reality where virtual characters interact with physical actors.
Unlike scripted projections, Ark AR driven performances can respond to movement and timing. If an actor pauses, the digital environment adjusts. If the audience shifts perspective, the scene remains coherent.
Artists have long explored augmented spaces. What changes now is responsiveness. As curator Hans Ulrich Obrist observed in a 2020 conversation on immersive art, “The medium becomes interesting when it reacts, not when it repeats.” Ark AR embodies that principle.
Museums and galleries experiment with adaptive exhibits that personalize content. Educational storytelling becomes participatory rather than linear.
How Ark AR Differs from Traditional AR
The distinction between traditional AR and Ark AR becomes clear when comparing capabilities.
| Aspect | Traditional AR | Ark AR |
|---|---|---|
| Scene creation | Predefined anchors and markers | Knowledge inferred dynamic scenes |
| Adaptability | Limited to scripted cases | Responds to novel environments |
| Intelligence | Basic tracking and rendering | Contextual reasoning and memory |
| Hardware | Often specialized devices | Standard devices with cloud support |
| Scalability | High setup cost | Flexible deployment |
Traditional systems excel in predictable settings. Ark AR thrives in uncertainty. By inferring context rather than relying on fixed data, it handles change gracefully.
This difference mirrors shifts in AI more broadly. Rule based systems gave way to learning systems. AR is following a similar trajectory.
Performance and Technical Challenges
Despite its promise, Ark AR faces challenges. Low latency remains critical. Cloud dependence introduces network variability. Privacy concerns arise when environments are continuously scanned.
Research from the ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology emphasizes the importance of edge computing for AR. By processing data locally when possible, Ark AR systems mitigate latency while still leveraging cloud intelligence.
Occlusion handling and drift reduction remain active research areas. Ark AR’s inference based approach helps, but physics still matters. Digital objects must obey visual rules to feel real.
Ethical considerations also emerge. Knowledge driven AR could influence perception. Designers must ensure transparency and avoid manipulative overlays.
As researcher Mark Billinghurst wrote in IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, “AR systems mediate reality. That mediation carries responsibility.”
Expert Perspectives
“Context awareness is the missing piece in most AR deployments,” said Dr. Helen Papagiannis, an AR researcher and author, in a 2022 interview with Forbes. “Systems like Ark point toward AR that understands why content matters, not just where it goes.”
From an enterprise standpoint, Accenture’s extended reality lead Tom Lounibos noted in a 2021 report that scalable AR requires cloud integration and AI. “The future is adaptive, not scripted,” he said.
Academic researchers echo this view. In a 2023 arXiv paper, the ArK authors concluded that knowledge transfer from foundation models enables “emergent AR behaviors without environment specific training.”
Together, these perspectives frame Ark AR as a convergence of trends rather than a single product.
Timeline of Key Developments
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1997 | Azuma defines core AR principles |
| 2010 | Mobile AR frameworks gain traction |
| 2016 | Major tech firms invest in AR platforms |
| 2020 | Cloud assisted AR becomes viable |
| 2023 | ArK framework introduces knowledge driven AR |
| 2024 | Enterprise pilots expand adaptive AR use |
This progression shows steady movement toward intelligence and scale.
Takeaways
- Ark AR integrates AI driven knowledge inference into augmented reality systems.
- It shifts AR from static overlays to adaptive, context aware experiences.
- Enterprise training and marketing see immediate benefits.
- Creative fields gain responsive storytelling tools.
- Cloud infrastructure enables scalability with standard devices.
- Ethical and performance challenges remain important considerations.
Conclusion
I see Ark Augmented Reality as less a single technology and more a direction. It reflects a broader shift toward systems that interpret the world rather than merely decorate it. By combining spatial computing with knowledge inference, Ark AR moves closer to experiences that feel intuitive and resilient.
This matters because AR’s success depends on trust. Users must believe that digital content belongs in their environment. When overlays adapt intelligently, that trust grows. When systems fail gracefully in unfamiliar spaces, adoption follows.
Ark AR will not replace traditional AR overnight. Scripted experiences still have their place. But as environments grow more complex and expectations rise, adaptive systems will define the next chapter.
The augmented future is not about adding more layers. It is about understanding the layers that already exist.
FAQs
What is Ark Augmented Reality?
Ark AR refers to advanced augmented reality platforms that use AI driven knowledge inference to create adaptive, real time overlays in physical environments.
How is Ark AR different from standard AR?
Standard AR relies on predefined anchors. Ark AR interprets context using machine learning, allowing it to generate scenes in unfamiliar environments.
Does Ark AR require special hardware?
Most Ark AR systems run on standard smartphones or tablets, using cloud infrastructure to handle complex computation.
What industries benefit most from Ark AR?
Enterprise training, education, marketing, and immersive arts see strong benefits due to adaptability and scalability.
Is Ark AR commercially available?
Elements of Ark AR exist in research frameworks and enterprise pilots, with broader commercialization emerging gradually.